监听是一个目录,这个目录不能有子目录,监控的是这个目录下的文件。采集完成,这个目录下的文件会加上后缀(.COMPLETED)
配置文件:
一个NetCat Source用来监听一个指定端口,并将接收到的数据的每一行转换为一个事件。
数据源: netcat(监控tcp协议)
Channel:内存
数据目的地:控制台
配置文件
#指定代理 a1.sources = r1 a1.channels = c1 a1.sinks = k1 #指定sources a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 #指定source的类型 a1.sources.r1.type = netcat #指定需要监控的主机 a1.sources.r1.bind = 192.168.191.130 #指定需要监控的端口 a1.sources.r1.port = 3212 #指定channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory #sinks 写出数据 logger a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1 a1.sinks.k1.type=logger (3)Source---avro 监听AVRO端口来接受来自外部AVRO客户端的事件流。利用Avro Source可以实现多级流动、扇出流、扇入流等效果。另外也可以接受通过flume提供的Avro客户端发送的日志信息。
数据源: avro
Channel:内存
数据目的地:控制台
配置文件
source ====exec (一个Linux命令: tail -f)
channel====memory
sink====hdfs
注意:如果集群是高可用的集群,需要将core-site.xml 和hdfs-site.xml 放入flume的conf中。
配置文件:
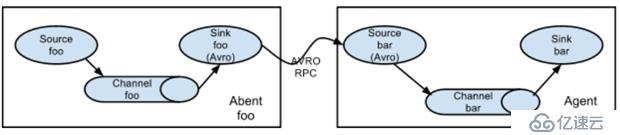
从第一台机器的flume agent传送到第二台机器的flume agent。
例:
规划:
hadoop02:tail-avro.properties
使用 exec “tail -F /home/hadoop/testlog/welog.log”获取采集数据
使用 avro sink 数据都下一个 agent
hadoop03:avro-hdfs.properties
使用 avro 接收采集数据
使用 hdfs sink 数据到目的地
配置文件 #tail-avro.properties a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /home/hadoop/testlog/date.log a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 #Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = avro a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop02 a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a1.sinks.k1.batch-size = 2 #Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 #avro-hdfs.properties a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = avro a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0 a1.sources.r1.port = 4141 #Describe k1 a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path =hdfs://myha01/testlog/flume-event/%y-%m-%d/%H-%M a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = date_ a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.maxOpenFiles = 5000 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize= 100 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat =Text a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 102400 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 1000000 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 (2)多路复用采集
郑重声明:本文版权归原作者所有,转载文章仅为传播更多信息之目的,如作者信息标记有误,请第一时间联系我们修改或删除,多谢。
